Embark on a journey into Python programming with “How to Code in Python: 10 Python Programming Tutorials for Beginners.” Discover the world of Python in an engaging and informative manner that showcases its importance and versatility.
Explore setting up your Python development environment, mastering Python basics and syntax, and much more in this comprehensive guide.
Introduction to Python Programming
Python is a high-level, versatile programming language known for its simplicity and readability. It is widely used in various fields such as web development, data science, artificial intelligence, automation, and more. Its ease of use and powerful libraries make it a popular choice among developers.
Popular Companies and Projects
- Google: Python is extensively used at Google for various applications, including web development, system administration, and more.
- Instagram: The backend of Instagram is primarily built using Python, showcasing its scalability and efficiency.
- Dropbox: Python is the main language behind the core functionality of Dropbox, demonstrating its reliability in handling large-scale projects.
Simplicity and Readability
Python code is known for its clean and easy-to-understand syntax, making it ideal for beginners and experienced programmers alike. The language emphasizes readability and simplicity, allowing developers to write code that is concise and efficient.
Versatility in Applications
- Web Development: Python’s frameworks like Django and Flask are popular choices for building dynamic websites and web applications.
- Data Science: Python’s libraries such as NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib make it a go-to language for data analysis, visualization, and machine learning.
- Automation: Python’s simplicity and extensive libraries enable developers to automate repetitive tasks and streamline workflows efficiently.
Setting Up Python Development Environment

Setting up your Python development environment is crucial to start coding efficiently. Here’s a guide on how to do it:
Installing Python on Different Operating Systems
Python can be installed on various operating systems. Here are the steps for each:
- For Windows:
Download the Python installer from the official website and follow the installation wizard.
- For Mac:
Mac OS comes with Python pre-installed. You can also download the latest version from the official website.
- For Linux:
Most Linux distributions come with Python pre-installed. You can use the package manager specific to your distribution to install Python.
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
IDEs like PyCharm, VS Code, or Jupyter Notebook provide a user-friendly interface for coding in Python. Here’s how to use them:
- Install the IDE of your choice from their respective websites.
- Open the IDE and create a new Python project or file to start coding.
- Utilize features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and debugging tools to enhance your coding experience.
Setting Up a Virtual Environment
Setting up a virtual environment for Python projects helps manage dependencies effectively. Follow these steps:
- Install the ‘virtualenv’ package using pip:
pip install virtualenv
- Create a new virtual environment:
virtualenv myenv
- Activate the virtual environment:
source myenv/bin/activate
Importance of Package Managers
Package managers like pip are essential for installing external libraries and packages in Python. Here’s why they are important:
- Allows you to easily install, update, and manage Python packages.
- Ensures that your projects have the required dependencies to run smoothly.
- Provides a centralized repository for Python packages, making it convenient to access a wide range of libraries.
Python Basics and Syntax

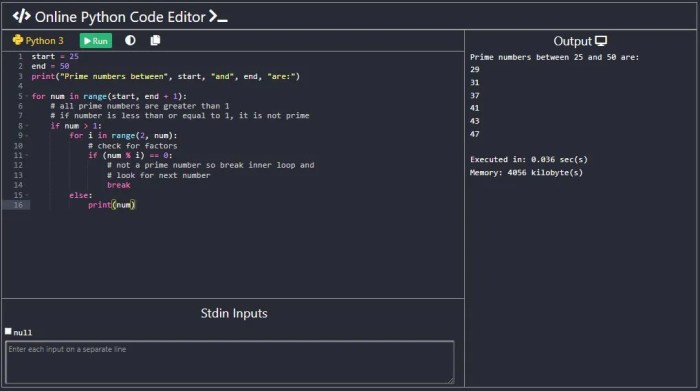
Python basics and syntax are essential to understand in order to write effective code. In this section, we will cover fundamental concepts such as variables, data types, operators, control flow structures, functions, lists, dictionaries, tuples, and the importance of indentation in Python.
Variables and Data Types
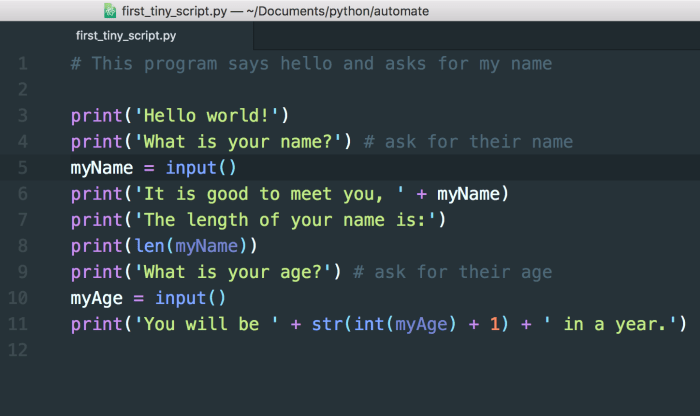
Variables in Python are used to store data values. They can be of different types such as integers, floats, strings, and booleans. Here is an example of defining variables in Python:
num1 = 10
name = “Alice”
is_true = True
Operators and Control Flow Structures
Operators in Python are symbols that perform operations on variables and values. Control flow structures like if statements and loops help in making decisions and repeating actions based on conditions. Here is an example of using operators and control flow structures:
if num1 > 5:
print(“Number is greater than 5”)
else:
print(“Number is less than or equal to 5”)
Functions in Python
Functions in Python are blocks of code that perform a specific task. They allow for code reusability and organization. Here is an example of defining and calling a function in Python:
def greet(name):
return “Hello, ” + nameprint(greet(“Bob”))
Working with Lists, Dictionaries, and Tuples
Lists, dictionaries, and tuples are data structures in Python that allow storing collections of data. Lists are ordered and mutable, dictionaries are unordered and mutable with key-value pairs, and tuples are ordered and immutable. Here is an example of working with these data structures:
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
my_dict = “name”: “Alice”, “age”: 30
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3)
Importance of Indentation in Python
Indentation plays a crucial role in Python for code readability and structure. It is used to define blocks of code within functions, loops, and conditional statements. Incorrect indentation can lead to syntax errors in Python. Here is an example showcasing the importance of indentation:
for i in range(5):
if i % 2 == 0:
print(i, “is even”)
else:
print(i, “is odd”)
Conclusive Thoughts
As we reach the end of our Python programming adventure, remember the key takeaways from these tutorials that will help you kickstart your coding journey with confidence and enthusiasm. Happy coding!